Technical cameras
InSight has two technical cameras
InSight's robotic arm IDA is fitted with a stereo colour camera (IDC) similar to the navigation cameras (NavCam) on the American Spirit and Opportunity rovers. Mounted on the segment corresponding to the forearm and near the elbow joint, it has a resolution of 1024 x 1024 pixels, and a 45° field of view. It is inclined at 20° to the arm, an angle that allows it to easily image the deck of the lander as well as its surroundings.
The IDC will be an essential aid during the various deployment stages, when InSight's main two instruments—the SEIS seismometer and the HP3 heat flow sensor—will be gently placed on the ground.
After landing, it will also allow engineers to inspect the probe’s deck and check the state of critical systems such as the solar arrays. Geologists will also be able to put it to good use by taking panoramic pictures of the Elysium Planitia, the probe’s landing site, and studying its geomorphology. In contrast to the IDC, InSight's second camera is immobile. The Instrument Context Camera (ICC) is riveted underneath the lander platform, facing the scientific instrument placement area at 45° to the horizontal. It too is derived from the cameras on the Spirit and Opportunity rovers, or more accurately, their hazard avoidance cameras (HazCam). It is a black and white wide-angle camera with a 124° field of view.
The ICC is designed to provide the best possible images of the area in front of the robotic arm, which will appear completely clear. Using the IDC’s stereo-pair images, engineers will be able to construct a 3D digital model of the Martian terrain. This model will then be used to accurately determine the most appropriate locations for setting down the instruments.
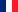
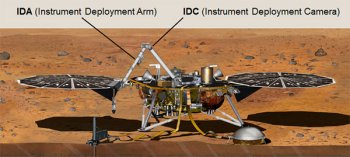 Locations of the IDC and ICC technical cameras on InSight (© NASA).
Locations of the IDC and ICC technical cameras on InSight (© NASA).
A colour camera for imaging the probe and its surroundings in stereo
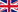
 The IDC camera mounted on the IDA robotic arm of InSight (© NASA/JPL-Caltech/IPGP/Philippe Labrot).
The IDC camera mounted on the IDA robotic arm of InSight (© NASA/JPL-Caltech/IPGP/Philippe Labrot).
Last updated: 28 October 2016
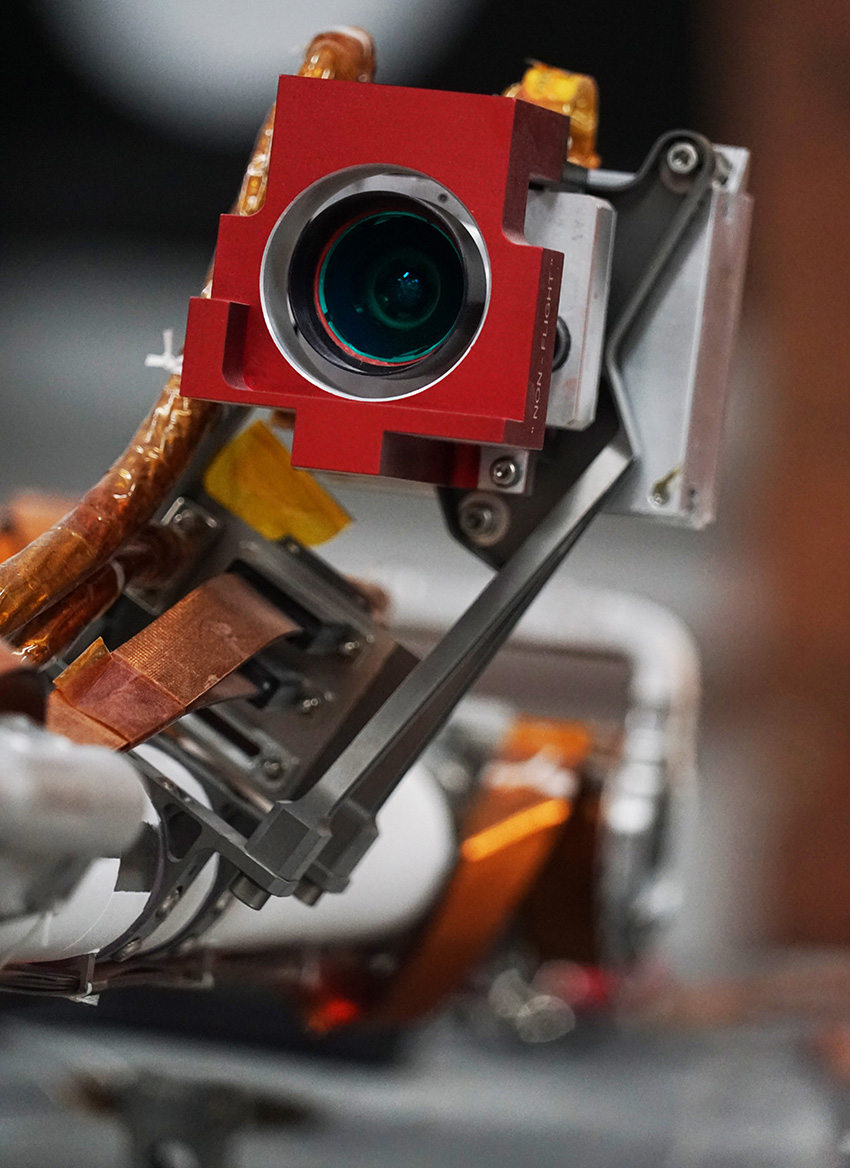
 The ICC technical camera on the InSight probe (© NASA).
The ICC technical camera on the InSight probe (© NASA).
Objective: imaging the instrument placement zone
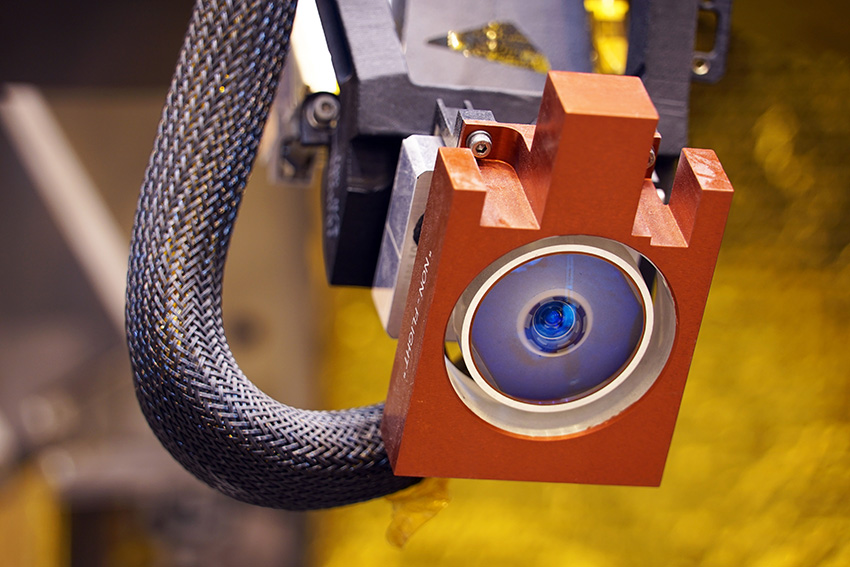 The ICC camera located under the InSight deck (© NASA/JPL-Caltech/IPGP/Philippe Labrot).
The ICC camera located under the InSight deck (© NASA/JPL-Caltech/IPGP/Philippe Labrot).
Last updated: 28 October 2016